Fuel Tank Baffles Explained: Why They Matter for Safety
Fuel tanks are the unsung heroes of transportation. Whether you’re driving a car, flying in an airplane, or cruising on a boat, fuel tanks store the energy that powers your journey. But here’s something you might not think about: fuel doesn’t just sit still. It moves around as you accelerate, brake, or navigate turns—a phenomenon known as fuel sloshing. And if left unchecked, this movement can lead to serious problems like engine starvation, reduced performance, or even catastrophic failures.
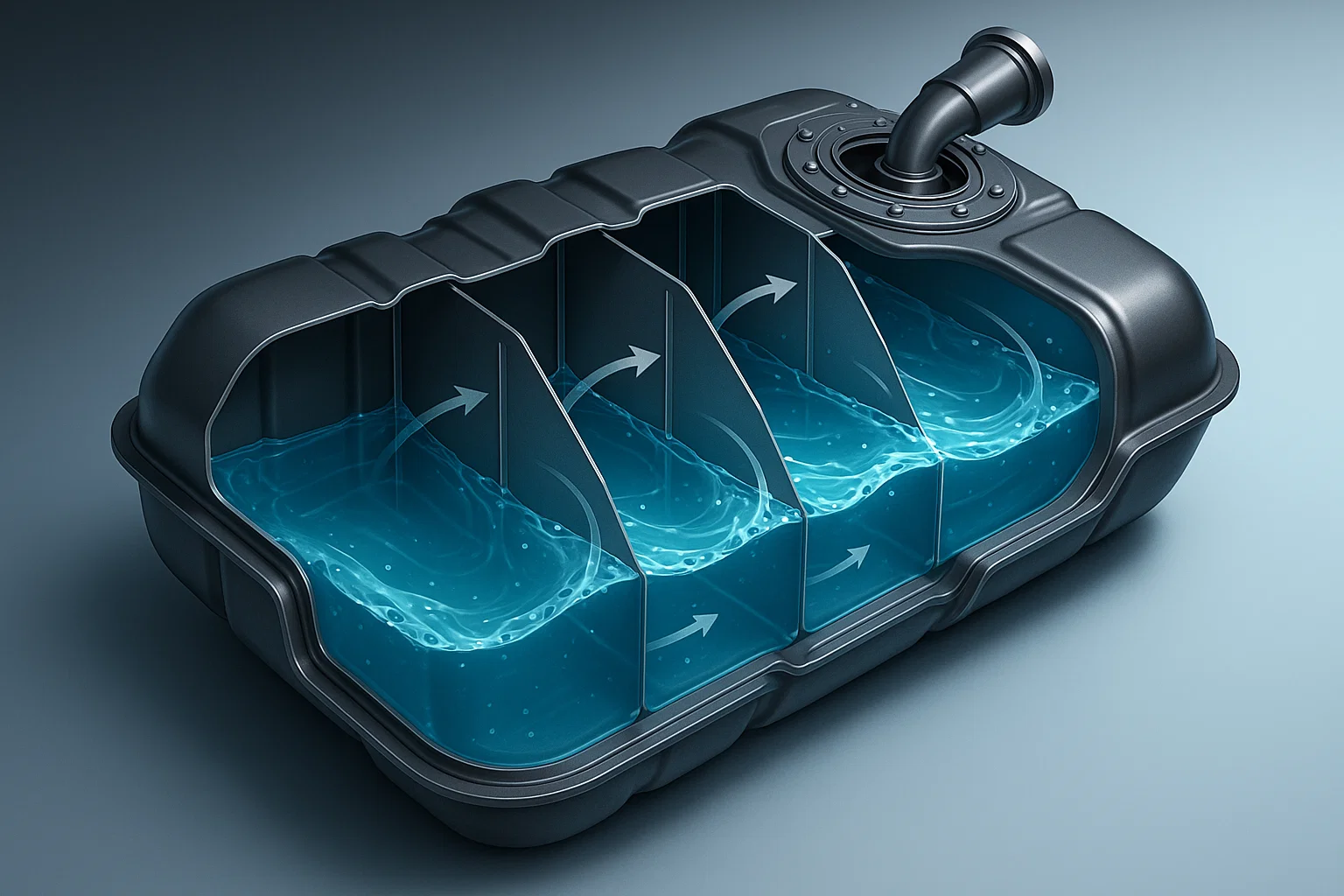
That’s where baffles come into play. These ingenious internal structures inside fuel tanks are designed to control fuel movement, ensuring safety, stability, and reliability. In this blog post, we’ll explore what baffles are, how they work, why they’re critical for safety, and what the future holds for this essential technology.
What Are Fuel Tank Baffles?
Definition
Baffles are internal partitions or barriers inside fuel tanks. Their primary job is to divide the tank into smaller compartments, limiting the amount of free space for fuel to slosh around.
Primary Function
The main purpose of baffles is simple but crucial: they prevent excessive fuel sloshing. By controlling fuel movement, baffles help maintain consistent fuel pickup, reduce structural stress, and minimize risks like fire or explosion.
Materials Used
- Metals: Aluminum and steel are popular choices due to their strength and heat resistance.
- Plastics & Composites: Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, these materials are increasingly used in modern vehicles.
Basic Design Principles
- Swirl Baffles: Redirect fuel flow to minimize turbulence.
- Honeycomb Structures: Provide structural integrity while allowing controlled movement.
- Check Valves (in some systems): Ensure one-way fuel flow to maintain consistent pickup.
Types of Fuel Tanks & Baffle Designs
A. Different Fuel Tank Structures
- Rigid Tanks: Found in cars, trucks, and many aircraft. These often use simple metal baffles.
- Flexible/Bladder Tanks: Common in aviation and motorsports, designed to deform without leaking. Baffles here must be flexible yet durable.
- Wet Wing Tanks: Integrated into aircraft wings, requiring specialized lightweight baffles to handle G-forces during flight maneuvers.
B. Baffle Variations by Application
- Automotive: Basic baffles focus on stability during everyday driving.
- Aviation: Advanced designs manage extreme forces during takeoff, landing, and turbulence.
- Marine: Corrosion-resistant baffles protect against saltwater exposure.
- Racing: High-performance fuel cells feature intricate baffling systems to handle rapid acceleration and deceleration.
How Do Baffles Work?
Baffles tackle several challenges associated with fuel sloshing:
- Preventing Sloshing: By dividing the tank into sections, baffles limit large-scale fuel movements.
- Maintaining Consistent Fuel Pickup: Ensures the fuel pump always has access to fuel, preventing engine starvation.
- Reducing Hydrodynamic Pressure: Minimizes stress on the tank walls caused by moving fuel.
- Minimizing Vapor Buildup: Lowers the risk of explosions or fires by stabilizing fuel levels.
Why Are Baffles Critical for Safety?
A. Preventing Fuel Starvation
Without baffles, sudden stops or sharp turns could cause fuel to surge away from the pickup point, leading to engine stalling. For example, race cars spinning out often experience fuel surge issues.
B. Reducing Fire & Explosion Hazards
Sloshing increases vapor release, creating an explosive environment. Baffles help stabilize fuel, reducing this risk significantly.
C. Improving Vehicle Stability
In cars, motorcycles, and boats, uncontrolled fuel movement shifts weight unpredictably, increasing rollover risks during sharp turns or rough seas.
D. Structural Protection
Fuel momentum under high-speed conditions can deform tanks over time. Baffles distribute pressure evenly, protecting the tank structure.
Engineering & Design Considerations
Designing effective baffles involves understanding fluid dynamics and balancing competing priorities:
- Fluid Dynamics: Placement and shape affect how well baffles control fuel movement.
- Trade-offs: Adding more baffles reduces available fuel capacity—a key consideration for long-distance applications.
- Computational Modeling: Modern engineers use simulations to optimize baffle designs for specific needs.
- Custom Solutions: High-performance applications demand tailored baffling systems that meet unique requirements.
Real-World Applications
- Automotive: SUVs and off-road vehicles rely on robust baffles for stability on uneven terrain. Race cars use advanced baffling to handle extreme conditions.
- Aviation: Commercial jets and military aircraft depend on precision-engineered baffles to manage fuel during complex maneuvers.
- Marine: Speedboats and yachts require corrosion-resistant baffles to withstand harsh marine environments.
- Industrial/Military: Heavy machinery and armored vehicles need durable baffles to operate reliably in demanding scenarios.
What Happens If Baffles Fail?
Failure of baffles can result in:
- Engine Cutouts: The fuel pump may suck air instead of fuel, causing stalling.
- Vehicle Instability: Weight shifts can increase rollover risks in trucks and SUVs.
- Aircraft Emergencies: Imbalanced fuel distribution can lead to wing imbalance or flameouts.
- Long-Term Damage: Uncontrolled fuel movement can deform tanks or weaken structural integrity.
Regulations & Industry Standards
Regulations ensure baffles meet strict safety criteria:
- Automotive: DOT/FMVSS standards mandate minimum baffling requirements.
- Aviation: FAA rules govern fuel tank design to prevent accidents.
- Motorsports: FIA and NASCAR enforce rigorous standards for race car fuel cells.
- Marine: USCG and ISO regulations cover baffling in boats and ships.
Maintenance & Inspection
Regular maintenance is crucial to ensure baffles function correctly:
- Signs of Failure: Listen for unusual sloshing noises, watch for fluctuating fuel gauges, and note engine sputtering during turns.
- Inspection Methods: Visual checks, pressure tests, and diagnostic tools help identify issues early.
- Repair/Replacement: Address rust, cracks, or loose baffles promptly. After major impacts, inspect the entire system thoroughly.
Innovations & Future Trends
The future of baffles looks promising with emerging technologies:
- Active Baffle Systems: Use electronics to dynamically adjust baffling based on real-time conditions.
- 3D-Printed Baffles: Enable lightweight, custom designs tailored to specific applications.
- Self-Healing Materials: Prevent corrosion and fatigue, extending baffle lifespan.
- Smart Fuel Tanks: Incorporate sensors to monitor fuel levels and baffle performance in real time.
Fuel tank baffles might not grab headlines, but they’re vital for safety, performance, and reliability across industries. Proper design, regular maintenance, and adherence to regulations ensure these unsung heroes do their job effectively. As technology advances, innovations like active systems and smart monitoring promise to make baffles even more effective.
Next time you hit the road, take to the skies, or set sail, remember the humble baffle quietly working behind the scenes to keep you safe.
FAQ Section
Got questions about fuel tank baffles? We’ve got answers! Below, we address some of the most common queries and debunk a few myths to help you better understand these critical components.
Q: Can you drive without baffles?
A: Technically, yes—you can drive without baffles. However, it’s not advisable. Without baffles, fuel sloshing becomes a significant issue. Imagine taking a sharp turn or braking suddenly—the fuel inside your tank will surge to one side, potentially starving the engine of fuel. This can lead to engine stalling, poor performance, or even dangerous situations like losing power during critical moments (e.g., merging onto a highway). For vehicles that experience frequent acceleration, deceleration, or cornering, baffles are essential for maintaining stability and safety.
Q: Do all fuel tanks have baffles?
A: Not all fuel tanks are equipped with baffles. Most modern vehicles, aircraft, and marine vessels include them because they operate in dynamic environments where fuel movement needs to be controlled. However, simpler systems—like small portable generators, lawnmowers, or older vehicles—may lack baffles. In these cases, the risk of fuel sloshing is minimal because the equipment is typically used in stable conditions or at low speeds. That said, for high-performance or safety-critical applications, baffles are almost always present.
Q: How do I know if my baffles are working properly?
A: There are a few telltale signs that your baffles might be failing or need attention:
- Unusual Sloshing Noises: If you hear loud sloshing sounds when turning, braking, or accelerating, it could indicate that the baffles aren’t doing their job.
- Fuel Gauge Fluctuations: A bouncing fuel gauge needle may suggest uneven fuel distribution caused by ineffective baffles.
- Engine Sputtering in Turns: If your engine hesitates or cuts out during sharp turns or sudden stops, it could mean the fuel pickup is being starved due to excessive sloshing.
If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s worth having your fuel system inspected by a professional.
Q: Can I add baffles to an existing fuel tank?
A: Yes, in many cases, you can retrofit baffles into an existing fuel tank. This is especially common in motorsports, off-roading, or aviation, where performance and safety are paramount. Retrofit baffles come in various forms, including foam inserts, custom partitions, or aftermarket baffled fuel cells. However, retrofitting should be done carefully to ensure compatibility with your vehicle’s design and regulatory requirements. Consulting a specialist is highly recommended.
Q: Are baffles only important for performance vehicles?
A: No, baffles are important for all types of vehicles, not just performance ones. While racing cars and high-speed boats benefit greatly from advanced baffling systems, everyday vehicles also rely on baffles for safe and reliable operation. For instance:
- Cars & Trucks: Prevent engine stalling during sharp turns or sudden stops.
- Boats: Reduce the risk of capsizing due to shifting weight caused by fuel movement.
- Aircraft: Ensure consistent fuel flow during takeoff, landing, and turbulence.
Even if you’re not pushing the limits of speed or agility, baffles still play a crucial role in maintaining stability and preventing accidents.
Myth-Busting
Myth: “Baffles reduce fuel efficiency.”
Fact: This is a common misconception, but it’s only partially true. Baffles may slightly reduce the total usable capacity of a fuel tank because they occupy space within the tank. However, this minor reduction in volume has virtually no impact on overall fuel efficiency. On the contrary, baffles improve efficiency indirectly by ensuring consistent fuel delivery to the engine, reducing the likelihood of stalling or misfires. The benefits of baffles—enhanced safety, stability, and reliability—far outweigh the negligible loss in tank capacity.
Myth: “Modern vehicles don’t need baffles because of advanced fuel systems.”
A: While modern vehicles have sophisticated fuel delivery systems, such as electronic fuel injection and multiple fuel pumps, baffles are still necessary. These systems work best when fuel levels remain stable. Without baffles, sloshing can disrupt fuel flow, leading to inconsistent performance. Advanced technology doesn’t eliminate the need for baffles; rather, it complements them to create a more reliable and efficient system.
Myth: “Baffles are only found in high-end vehicles.”
A: Not true! Baffles are standard in most vehicles, from economy cars to luxury SUVs. Their inclusion isn’t about cost—it’s about function. Even entry-level vehicles use baffles to meet basic safety and performance standards. The complexity and design of the baffles may vary depending on the application, but nearly every vehicle benefits from having them.
Myth: “You can’t see or inspect baffles, so they’re not worth worrying about.”
A: Just because baffles are hidden inside the fuel tank doesn’t mean they’re unimportant. Regular inspections are key to ensuring they’re functioning correctly. Mechanics can perform visual checks (if accessible), pressure tests, or diagnostic scans to assess baffle condition. Ignoring baffles until something goes wrong can lead to costly repairs or dangerous situations, so proactive maintenance is always recommended.
Final Thoughts
Fuel tank baffles might seem like a small detail, but they play a big role in keeping your vehicle running smoothly and safely. Understanding how they work—and addressing common misconceptions—can help you make informed decisions about maintenance, upgrades, and overall vehicle care. Still have questions? Drop us a comment below, and we’ll do our best to answer!