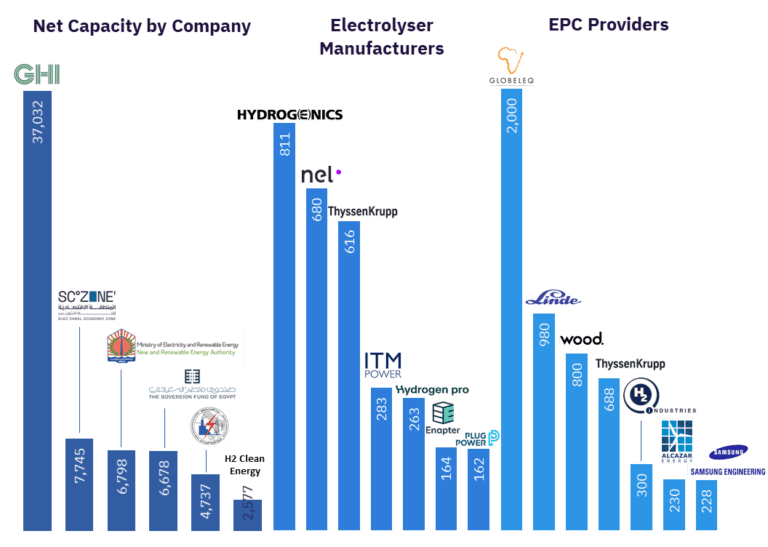
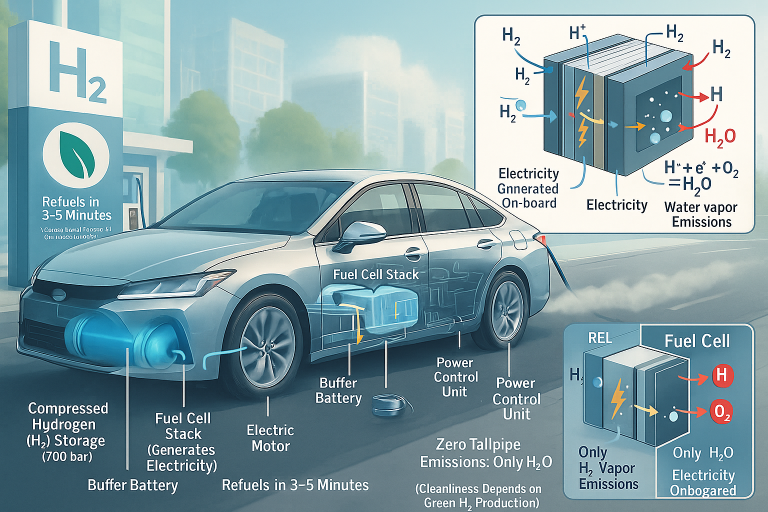
Exploring the Different Types of Hydrogen Energy: Advantages, Disadvantages, and Future Potential
Hydrogen energy is a clean and renewable source of energy that is gaining increasing attention as a potential solution to the world’s energy needs. There are several types of hydrogen energy, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. In this article, we will explore the different types of hydrogen energy and discuss some of the key considerations for each.
Thermal hydrogen is produced by heating natural gas or other hydrocarbons to create a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide. This mixture can then be separated to produce pure hydrogen. This process is often referred to as “gasification” and is one of the oldest and most well-established methods of hydrogen production. One of the key advantages of thermal hydrogen is that it can be produced using existing infrastructure and equipment, which makes it a relatively low-cost option. However, it also generates carbon dioxide as a byproduct, which can have negative environmental impacts.
Steam methane reforming is another common method of hydrogen production. This process involves combining natural gas and steam to produce hydrogen and carbon dioxide. The hydrogen produced in this way is often referred to as “grey hydrogen” because of the carbon dioxide emissions that are generated as a byproduct. However, this method of hydrogen production is also relatively low-cost and can be easily integrated into the existing natural gas infrastructure.
Electrolysis is a process that uses electricity to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. This method of hydrogen production is considered to be one of the most environmentally friendly, as it does not produce any greenhouse gas emissions. However, the cost of electricity is a major consideration when using electrolysis to produce hydrogen. Additionally, the efficiency of electrolysis is affected by the purity of the water used, as impurities can hinder the electrochemical reactions.
Biological hydrogen is produced by certain microorganisms that can convert organic matter into hydrogen. This process is known as “biological hydrogen production” and can be a sustainable and environmentally friendly method of hydrogen production. However, it requires specific conditions and infrastructure to be set up, which can be costly.
Photoelectrochemical hydrogen is another method of hydrogen production that uses solar energy to split water into hydrogen and oxygen. This process is considered to be one of the most sustainable and environmentally friendly methods of hydrogen production. However, the cost of the necessary equipment and infrastructure can be prohibitively expensive.
Nuclear hydrogen is produced by using nuclear energy to heat water and produce hydrogen. This method of hydrogen production is considered to be one of the most cost-effective, as nuclear power is relatively inexpensive. However, it also generates radioactive waste as a byproduct, which can have negative environmental impacts.
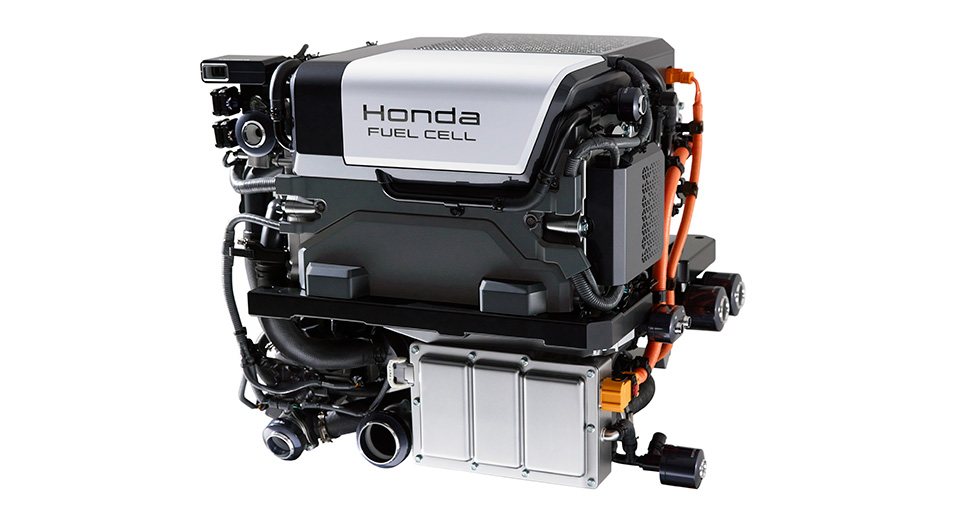
PEM fuel cells, also known as polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cells, is an electrochemical conversion device that converts the chemical energy of a fuel and an oxidant to electricity through an electrochemical reaction of a catalyst. These fuel cells are widely used in portable and transportation applications, such as forklifts and cars. They are also a key component in hydrogen infrastructure as they convert hydrogen into electricity.
Solid-state hydrogen storage is a new and promising method of hydrogen storage that involves using solid materials to store hydrogen at high densities. This allows for more efficient storage and transport of hydrogen fuel. The solid-state hydrogen storage technology is still in the development phase and it is expected to be safer and more efficient than traditional hydrogen storage methods such as compressed hydrogen and liquid hydrogen.
In conclusion, hydrogen energy is a clean and renewable source of energy that has the potential to play a key role in meeting the world’s energy needs. There are several types of hydrogen energy, each with its own unique characteristics and advantages. T