How Often Should You Change Generator Oil? A Complete Guide to Maximizing Performance and Longevity
Proper maintenance is the backbone of a reliable generator, ensuring it’s ready to power your home or business during outages. Among the most critical—and often neglected—tasks is changing the oil. This comprehensive guide dives deep into oil change frequency, factors that impact your schedule, and expert tips to extend your generator’s lifespan.
Why Regular Oil Changes Are Non-Negotiable
Generator engines operate under extreme conditions, relying on oil to:
- Lubricate moving parts (pistons, crankshafts, bearings) to minimize metal-on-metal friction.
- Dissipate heat generated by combustion and mechanical stress.
- Prevent corrosion by neutralizing acidic byproducts from fuel combustion.
- Trap contaminants like dirt, metal shavings, and carbon deposits.
Neglecting oil changes leads to:
- Sludge buildup, restricting oil flow and causing overheating.
- Accelerated engine wear, shortening the generator’s lifespan.
- Catastrophic failure during critical moments (e.g., storms, emergencies).
How Often Should You Change Generator Oil?
The answer depends on your generator’s type, usage, and environment. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
1. Generator Type and Usage Patterns
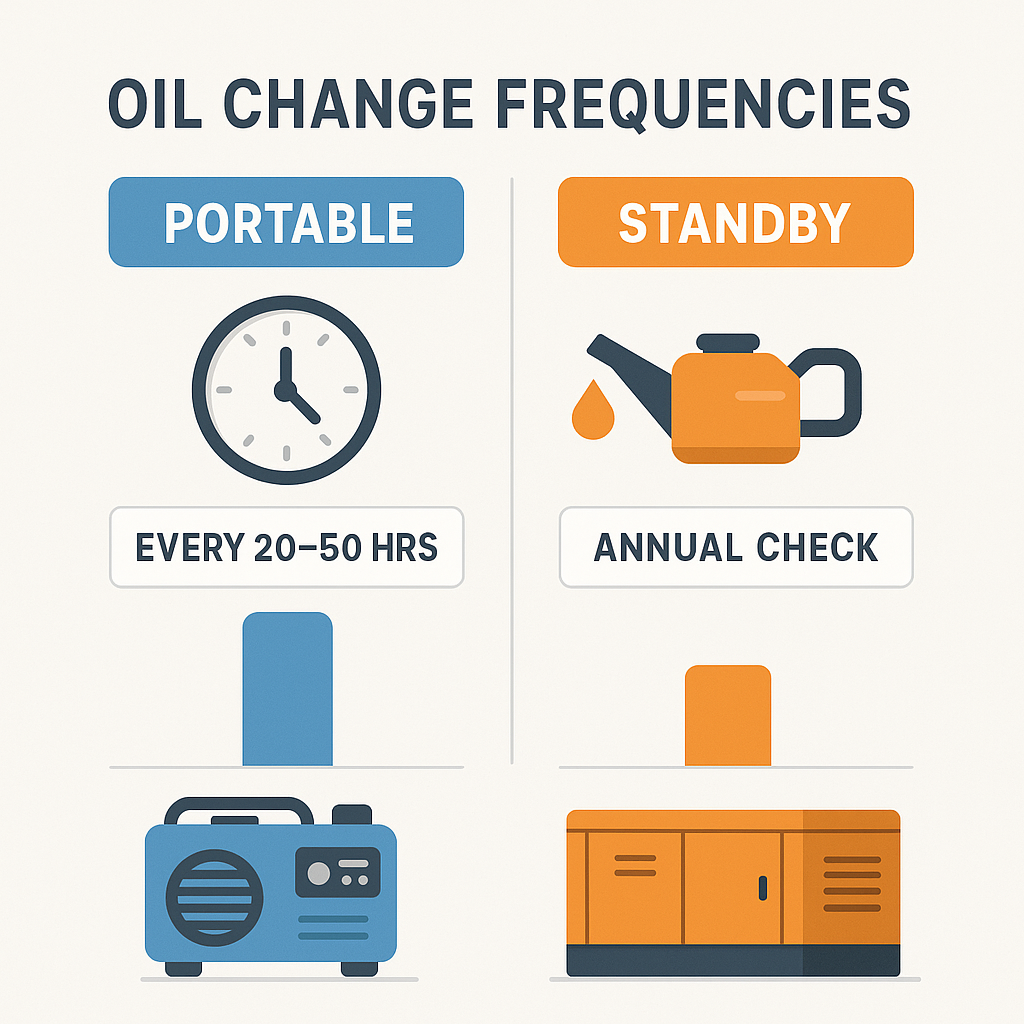
- Portable Generators (Used intermittently for camping, tailgating, or backup):
- Every 20–50 hours of runtime.
- Annually if unused (old oil degrades even when idle).
- Standby/Whole-House Generators (Automatic, high-capacity units):
- Every 100–200 hours or as specified by the manufacturer.
- Bi-annually if rarely activated (e.g., in areas with stable power grids).
- High-Load Scenarios (Powering heavy machinery, HVAC systems, or construction sites):
- Change oil 25–50% sooner than standard intervals due to prolonged stress.
2. Oil Type Matters
- Conventional Oil: Affordable but breaks down faster. Replace every 20–30 hours.
- Synthetic Oil: Resists thermal breakdown, lasts 50–100 hours, and excels in extreme heat or cold.
- Synthetic Blend: A mid-tier option offering better protection than conventional oil (up to 75 hours).
3. Environmental Factors
- Heat: High temperatures thin oil, reducing its lubricating properties.
- Dust/Dirt: Particulates infiltrate the oil, accelerating wear.
- Humidity: Moisture causes sludge and corrosion.
- Altitude: Thin air at high elevations strains engines, demanding more frequent changes.
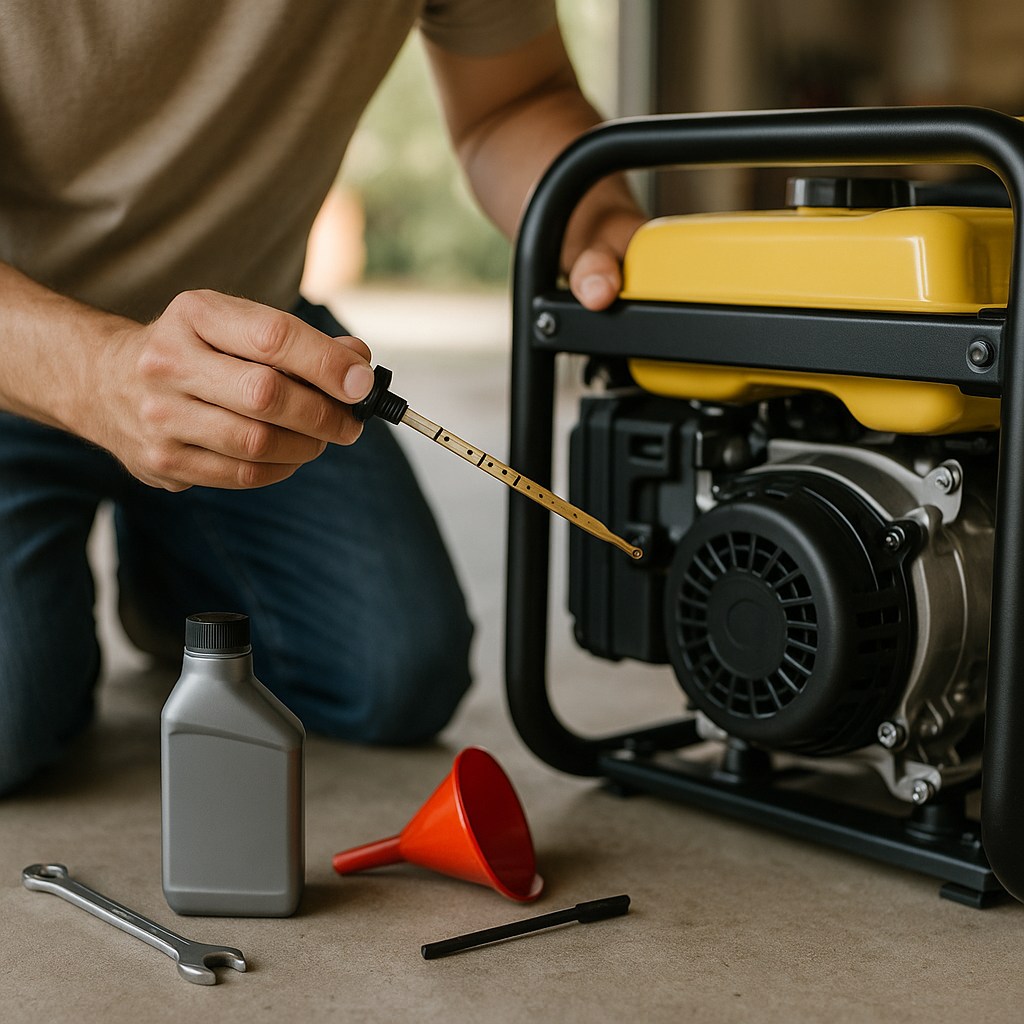
Step-by-Step: How to Check and Change Generator Oil
Checking Oil Quality and Level
- Safety First: Turn off the generator and let it cool for 15–20 minutes.
- Locate the Dipstick: Wipe it clean, reinsert fully, then check the level against markings.
- Inspect for Contaminants:
- Milky Oil: Indicates water/coolant leakage (common in humid climates).
- Gritty Texture: Signals dirt or metal particles.
- Dark, Thick Oil: Oxidation and carbon buildup mean it’s time for a change.
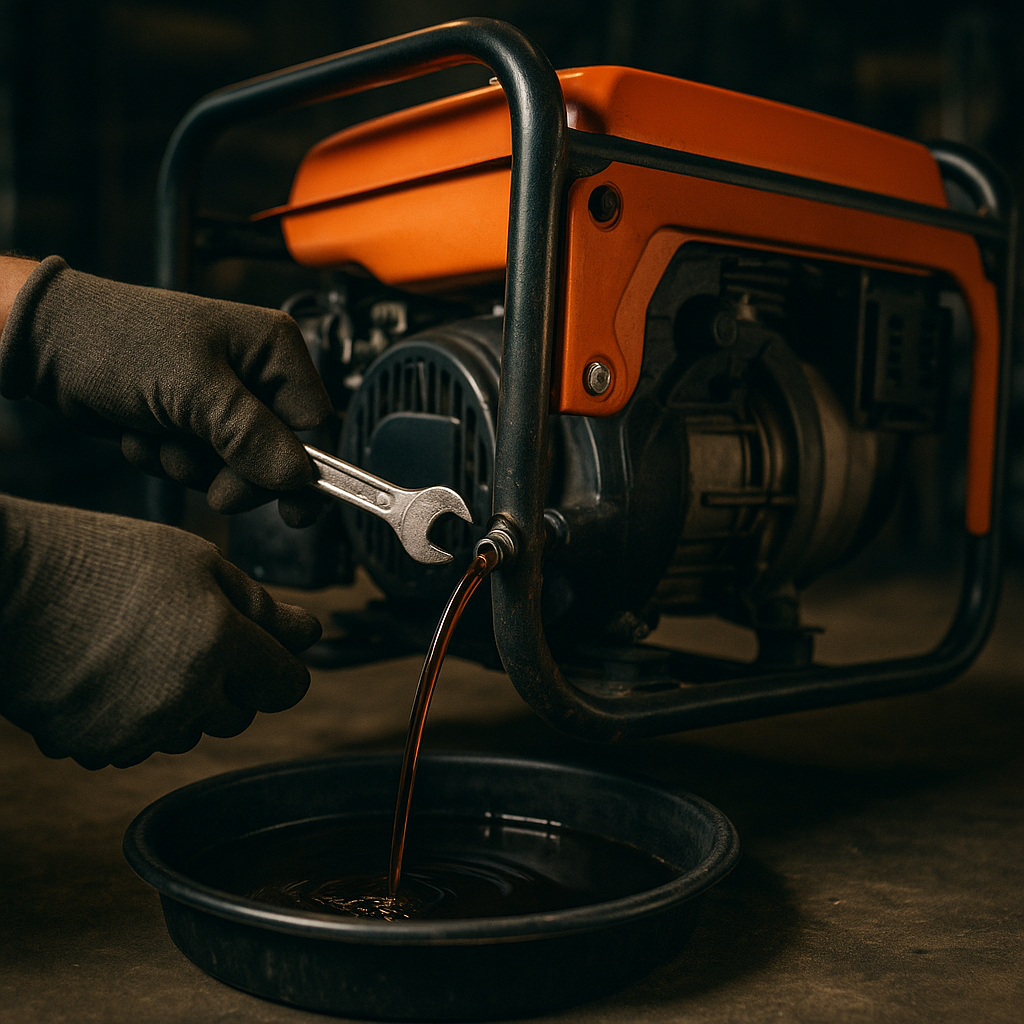
Changing the Oil
Tools Needed: Oil drain pan, socket wrench, funnel, gloves, replacement oil and filter.
Steps:
- Drain Old Oil: Position the drain pan under the plug. Remove the plug and let oil flow completely.
- Replace the Oil Filter (if equipped): Use a filter wrench to remove the old one. Lubricate the new filter’s gasket before installing.
- Refill with Fresh Oil: Use the viscosity recommended in your manual (e.g., SAE 10W-30 for most climates). Avoid overfilling—check the dipstick as you pour.
- Dispose Responsibly: Take used oil to a recycling center—never dump it!

Choosing the Right Oil for Your Generator
Viscosity Guidelines
- SAE 30: Ideal for warm climates (above 40°F/4°C).
- 10W-30: All-season oil for fluctuating temperatures.
- Synthetic 5W-30: Best for cold climates (below freezing).
2-Stroke vs. 4-Stroke Engines
- 4-Stroke: Use standard motor oil (no fuel mixing).
- 2-Stroke: Mix oil with gasoline at the ratio specified in your manual (e.g., 50:1).
Maintenance Schedule: Beyond Oil Changes
Keep your generator in peak condition with this checklist:
| Runtime Hours | Tasks |
|---|---|
| Every 20 Hours | Check oil level, inspect for leaks. |
| Every 50 Hours | Change oil, replace filter, inspect air filter. |
| Every 100 Hours | Test spark plugs, clean fuel injectors, check battery charge. |
| Annually | Run diagnostics, inspect fuel lines, test under load. |
5 Costly Mistakes to Avoid
- Using Automotive Oil: Car oils lack additives for small engines.
- Skipping the Filter: Not all generators have filters, but if yours does, replace it every other oil change.
- Ignoring the Manual: Honda, Generac, and other brands have unique requirements.
- Overfilling: Excess oil causes foaming and pressure buildup.
- Storing with Old Oil: Drain oil before long-term storage to prevent corrosion.
FAQs: Your Generator Oil Questions Answered
Q: Can I reuse oil if it looks clean?
A: No—oil degrades chemically even if it appears clear.
Q: What if my generator doesn’t have an hour meter?
A: Track runtime manually or invest in an aftermarket hour meter.
Q: Can synthetic and conventional oils be mixed?
A: Avoid mixing—stick to one type to prevent additive conflicts.
Final Pro Tips
- Keep a Log: Note oil changes, filter replacements, and issues.
- Pre-Run Checks: Always inspect oil before starting the generator.
- Invest in Quality: OEM filters and synthetic oil pay off in longevity.


