Can I use a portable generator to power my electric furnace?
When a power outage strikes, finding an alternative power source to keep your home comfortable becomes a top priority. One common question among homeowners is whether a portable generator can safely and effectively power an electric furnace. The answer isn’t a simple yes or no—it involves understanding your furnace’s energy needs, ensuring your generator meets those needs, and following strict safety protocols. Below is an expanded, step-by-step guide to help you assess if a portable generator is a viable solution for powering your electric furnace.
1. Assessing Your Electric Furnace’s Power Needs
Before you consider connecting your furnace to a portable generator, you must determine its power requirements. Electric furnaces typically draw a significant amount of power due to the demands of heating elements, blower motors, and control systems. These requirements are usually listed in the furnace’s documentation or on a specification label. Key points include:
- Wattage and Amperage: Understand both the wattage (total power) and amperage (current draw) requirements. This ensures you can compare these numbers with your generator’s output.
- Startup Surge: Many electric appliances, including furnaces, may draw extra power on startup. It’s essential to account for this surge to avoid overloading your generator.
By gathering this information, you create a baseline that helps you determine the capacity your generator must have.
2. Matching Generator Output with Furnace Requirements
Once you know the power requirements of your furnace, the next step is ensuring your portable generator can handle that load. Here’s what to consider:
- Generator Wattage: Portable generators are rated in watts. Compare the continuous and peak wattage output of your generator with the furnace’s requirements.
- Load Matching: For example, if your electric furnace requires 4,000 watts, a generator rated at 6,000 watts would provide a comfortable margin. However, if both the furnace and the generator are at the same wattage (e.g., 6,000 watts each), you must be extra cautious about potential overload during peak usage.
- Efficiency and Headroom: Always allow for some extra capacity to accommodate any unexpected surges or additional loads that might be present during a power outage.
Matching these figures accurately is crucial to ensure that the generator can handle the furnace without being overtaxed.
3. Critical Safety Considerations
Using a portable generator to power an electric furnace is possible, but safety must be your foremost concern. Consider the following precautions:
- Ventilation: Portable generators emit carbon monoxide (CO), a dangerous and odorless gas. Always operate your generator outdoors or in a well-ventilated area away from windows and doors to prevent CO buildup indoors.
- Location and Environment: Position the generator on a stable, dry surface. Ensure it is far from combustible materials such as paper, gasoline, or flammable liquids.
- Proper Grounding: To reduce the risk of electrical shock or fire, it’s essential that the generator is correctly grounded. This may require professional assessment or installation.
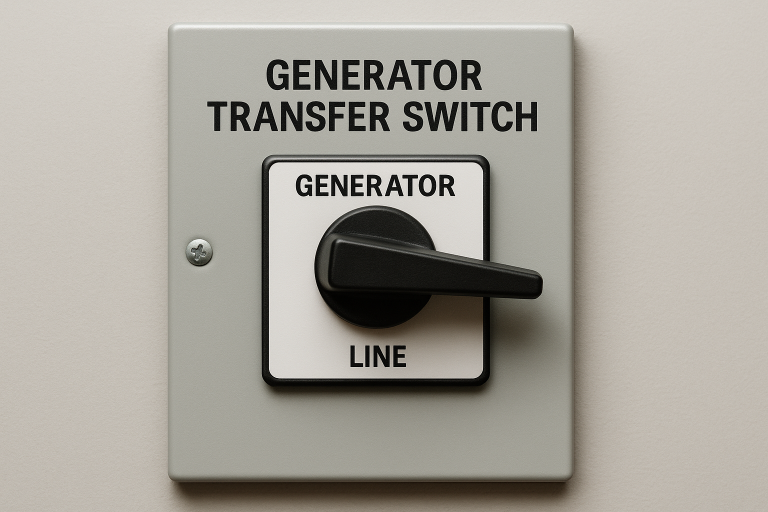
- Transfer Switch Installation: To prevent dangerous backfeeding (which can harm utility workers), consider installing a transfer switch. This device safely isolates your home’s electrical system from the utility grid when running on generator power.
By following these guidelines, you help create a safer environment for yourself and your household during power outages.
4. The Importance of Professional Installation
While DIY setups might seem appealing, the complexity of safely integrating a generator with your home’s electrical system typically warrants professional help:
- Expert Evaluation: A licensed technician can evaluate your furnace’s power requirements, the capacity of your generator, and your home’s overall electrical configuration.
- Safe Wiring Practices: Professional installation ensures that all wiring is done to code, reducing the risk of electrical hazards such as fires or electrocution.
- System Configuration: Technicians can properly configure the necessary transfer switches and safety mechanisms, ensuring seamless and safe operation during an outage.
Investing in professional installation is a small price to pay for the added safety and peace of mind it offers.
Real-World Examples
Example 1:
Imagine you have an electric furnace that requires 4,000 watts, and your portable generator is rated at 6,000 watts. In this scenario, the generator has sufficient capacity to power the furnace, with additional headroom to manage startup surges and potential extra loads.
Example 2:
Now, consider a situation where both your furnace and generator are rated at 6,000 watts. While technically the generator can meet the demand, the lack of extra capacity means you need to be vigilant about any additional loads or startup surges. In such cases, extra attention to safety protocols (especially regarding ventilation and grounding) becomes even more critical.
Conclusion
In summary, powering an electric furnace with a portable generator is indeed possible—but it requires careful planning and attention to detail. Start by thoroughly assessing your furnace’s power requirements, then match those needs with a generator that not only meets but ideally exceeds the wattage demands. Prioritize safety by ensuring proper ventilation, grounding, and installation of necessary electrical components like transfer switches. Lastly, engaging a professional to handle the installation can help you avoid electrical hazards and ensure compliance with local codes.
Remember, while a portable generator can serve as a reliable backup during emergencies, it is not designed as a long-term substitute for your primary power source. Use this solution only when necessary, and always follow safety guidelines to protect both your home and your family.