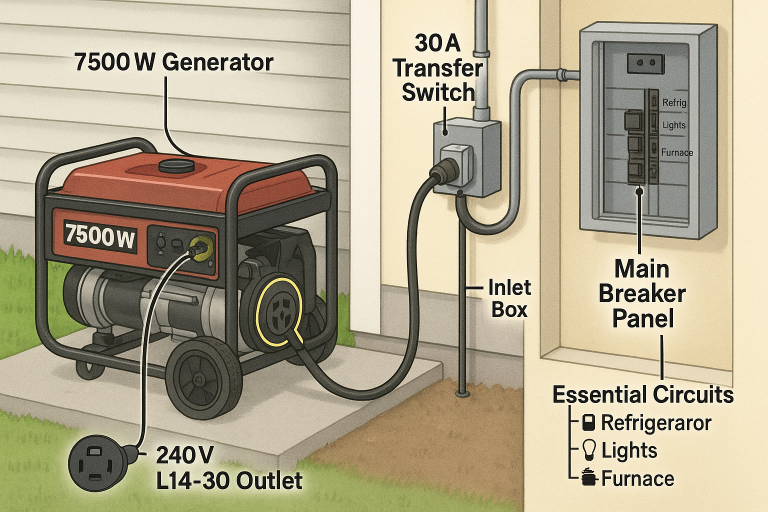
Can I use a portable generator to power my electric car?
As electric vehicles (EVs) continue to gain popularity, many owners seek alternative charging methods—especially in situations where traditional charging stations are unavailable. One common question is whether a portable generator can be used to charge an electric car.
The short answer is yes, it is technically possible. However, using a portable generator to charge an EV is far from practical due to numerous limitations, including inefficiency, low power output, high operating costs, and safety risks. In this article, we’ll explore why a portable generator isn’t a viable everyday charging solution and discuss better alternatives for keeping your EV charged and ready to go.
Why Charging an Electric Car with a Portable Generator Is Not Practical
While portable generators can provide emergency power in outages or remote locations, they are not designed for sustained, high-demand applications like charging electric vehicles. Here’s why:
1. Inefficiency and Energy Loss
Portable generators operate with internal combustion engines, which are inherently less efficient than electric grid power. Most generators run on gasoline, diesel, or propane, and the process of converting fuel into electricity involves significant energy loss due to heat and mechanical inefficiencies.
On the other hand, dedicated EV charging stations are built to maximize efficiency—delivering a direct and optimized power flow to your vehicle’s battery with minimal energy waste.
Key issue: A portable generator will consume more fuel per unit of electricity generated compared to grid power, making it an inefficient charging method.
2. Limited Power Output and Slow Charging
One of the biggest challenges with using a portable generator is its power capacity. Most consumer-grade portable generators produce power in the range of 1 kW to 5 kW, while an electric vehicle typically requires much more power for effective charging.
- Level 1 Charging (120V): Requires around 1.4 kW for a slow charge (12-20 hours for a full battery).
- Level 2 Charging (240V): Requires 3.3 kW to 22 kW (6-8 hours for a full charge).
- DC Fast Charging (Level 3): Requires 50 kW to 350 kW, which is far beyond what any portable generator can provide.
For example, if your EV battery has a 60 kWh capacity, and you’re using a 5 kW generator, it would take over 12 hours to fully charge—assuming 100% efficiency, which isn’t the case. In reality, power losses and inefficiencies in conversion could extend charging time to 15-20 hours or more.
Key issue: Most portable generators are simply too weak to charge an EV efficiently, and charging times would be impractically long.
3. High Operational Costs
Running a generator for an extended period can be expensive due to fuel consumption and maintenance needs. Let’s break it down:
- A 5,000-watt generator running on gasoline consumes about 0.75 gallons per hour.
- If charging takes 15 hours, that’s 11.25 gallons of gasoline needed.
- At an average fuel cost of $4 per gallon, that adds up to $45 per charge—far more expensive than using grid power, which might cost $10-$15 for a full charge.
Moreover, portable generators require regular maintenance, such as oil changes, air filter replacements, and spark plug servicing. These additional costs make it an expensive long-term charging option.
Key issue: Charging with a portable generator is far more expensive than using a home charger or public charging station.
4. Safety and Environmental Concerns
Portable generators emit harmful gases, including carbon monoxide (CO), which is a serious health hazard when used in enclosed spaces. This is why they must always be operated outdoors—never inside a garage, basement, or near open windows.
Additionally:
- Noise pollution: Generators can be very loud, typically running at 60-90 decibels, which can be disruptive in residential areas.
- Emissions: Gasoline and diesel generators release CO₂, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
- Fuel storage risks: Storing gasoline or diesel poses fire hazards if not handled properly.
Key issue: Generators pose safety risks due to carbon monoxide poisoning, fire hazards, and noise pollution, making them unsuitable for routine EV charging.
Better Alternatives for Charging an Electric Car
Since using a portable generator is not practical, let’s explore more efficient and cost-effective options for keeping your EV charged.
1. Public Electric Car Charging Stations
EV charging infrastructure is growing rapidly, with thousands of charging stations available worldwide. These stations offer different levels of charging:
- Level 1 Charging (120V): Typically found in homes and some public areas. Slow charging (12-20 hours for full charge).
- Level 2 Charging (240V): Common at shopping centers, workplaces, and parking lots. Provides a full charge in 6-8 hours.
- Level 3 DC Fast Charging (480V+): Found along highways and in urban centers. Can charge an EV up to 80% in 30 minutes.
Using public charging stations is convenient, reliable, and much faster than relying on a generator.
2. Home Charging Stations (EVSE – Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment)
Installing a home charging station is one of the best long-term solutions for EV owners. Here’s why:
✅ Convenient: Charge overnight while you sleep.
✅ Faster charging: Home Level 2 chargers deliver 3.3 kW to 22 kW, charging your EV in 6-8 hours.
✅ Cost-effective: Electricity from the grid is much cheaper than fuel for generators.
Most modern EVs support smart charging, allowing you to schedule charging during off-peak hours when electricity rates are lower, further reducing costs.
3. Solar Power: A Sustainable EV Charging Option
For those looking for an eco-friendly alternative, solar power can be an excellent solution. By installing solar panels on your home or property, you can:
☀️ Generate renewable energy to charge your EV.
💰 Reduce electricity bills and reliance on the grid.
🌍 Lower your carbon footprint by using clean energy.
Some EV owners pair solar panels with home battery storage (e.g., Tesla Powerwall) to store excess energy for nighttime charging.
Conclusion: The Best Way to Charge Your EV
While a portable generator can technically charge an electric car, it is not a practical or efficient solution due to:
- Inefficiency and energy loss
- Extremely slow charging times
- High fuel and maintenance costs
- Significant safety and environmental risks
Instead, better options for EV charging include:
✅ Public charging stations (fast, widely available, and convenient)
✅ Home charging stations (cost-effective and reliable)
✅ Solar power (sustainable and long-term savings)
By choosing the right charging method, EV owners can ensure safe, efficient, and cost-effective power for their vehicles—without the risks and drawbacks of using a portable generator. 🚗⚡