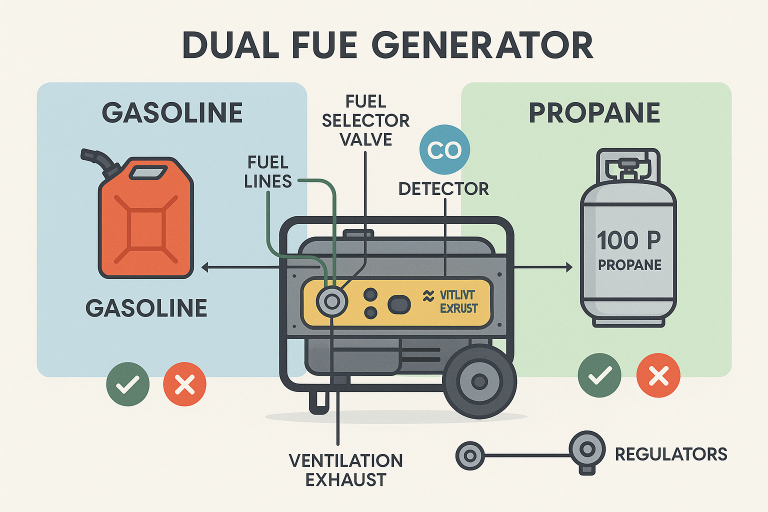
Can Generators Be Used Indoors?
Using a power generator indoors can be a convenient way to provide electricity during an outage or other emergency situations. However, it is important to follow proper safety guidelines to prevent carbon monoxide poisoning and other hazards.
WARNING: Power generators produce lethal amounts of carbon monoxide and should never be used inside a building or in enclosed spaces such as garages, basements, porches, crawlspaces, or sheds, or in partly-enclosed spaces such as carports or breezeways. Using a generator indoors can result in immediate death.
To ensure your safety, always place generators outside, at a distance, and downwind from any structures. Failure to follow these guidelines can lead to fatal carbon monoxide poisoning.
Carbon monoxide (CO) is a colorless, odorless gas that is produced by the incomplete burning of fossil fuels. When inhaled, CO can cause symptoms such as headache, dizziness, weakness, nausea, and even death in severe cases. Generators are a common source of CO, as they produce gas when burning fuel to generate electricity.
If you have to use a power generator indoors, follow these guidelines:
- Make sure the generator is properly ventilated: Keep the area around the generator clear of debris and do not use the generator in an enclosed space such as a basement or garage.
- Use a carbon monoxide detector: Install a battery-powered or battery-backup carbon monoxide detector in the area where the generator will be used. This will alert you if CO levels become dangerous.
- Only use the generator in a dry area: Do not use the generator in damp or wet conditions, as this can increase the risk of electrocution. If the generator gets wet, turn it off and allow it to dry completely before using it again.
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions: Read and follow all of the manufacturer’s instructions and guidelines for the safe operation of the generator. This includes proper installation, maintenance, and use of the generator.
In addition to the above guidelines, there are several other steps you can take to reduce the risk of CO poisoning when using a power generator indoors:
- Keep windows and doors open: To help ventilate the area where the generator is being used, keep windows and doors open. This will help to dissipate CO and other fumes produced by the generator.
- Use a generator-safe extension cord: If you need to use an extension cord to power appliances or devices with the generator, make sure it is rated for use with generators. Normal extension cords may not be able to handle the high current and voltage produced by a generator, which can lead to overheating and fire.
- Avoid using the generator for an extended period of time: If possible, only use the generator for short periods of time and have a backup plan in place for longer outages. Prolonged use of a generator can increase the risk of CO buildup and other hazards.
- Consider using a portable generator shelter: If you must use a generator indoors, consider purchasing a portable generator shelter. These are tents or enclosures specifically designed to house a generator and help ventilate CO and other fumes.
It is generally recommended to use a power generator outdoors, rather than indoors, if possible. This will help to reduce the risk of CO poisoning and other hazards. If you must use a generator indoors, make sure to follow the above guidelines and take all necessary precautions to ensure the safety of yourself and those around you.