Why Is My Electricity Bill So High? Hidden Factors Explained
You open your latest electricity bill and feel a sinking feeling in your stomach. It’s gone up again — and this time, it’s even higher than last month. But wait… you haven’t changed your habits. You’re not running the AC any more than before. So what gives?
You’re not alone. Across the United States, people are seeing their energy bills rise faster than ever. In fact, electricity prices have increased by 4.5% over the past year, which is nearly double the overall inflation rate. And experts say these costs will keep rising through at least 2026.
Let’s break down why your bill might be so high and what you can do about it — both inside your home and beyond your control.
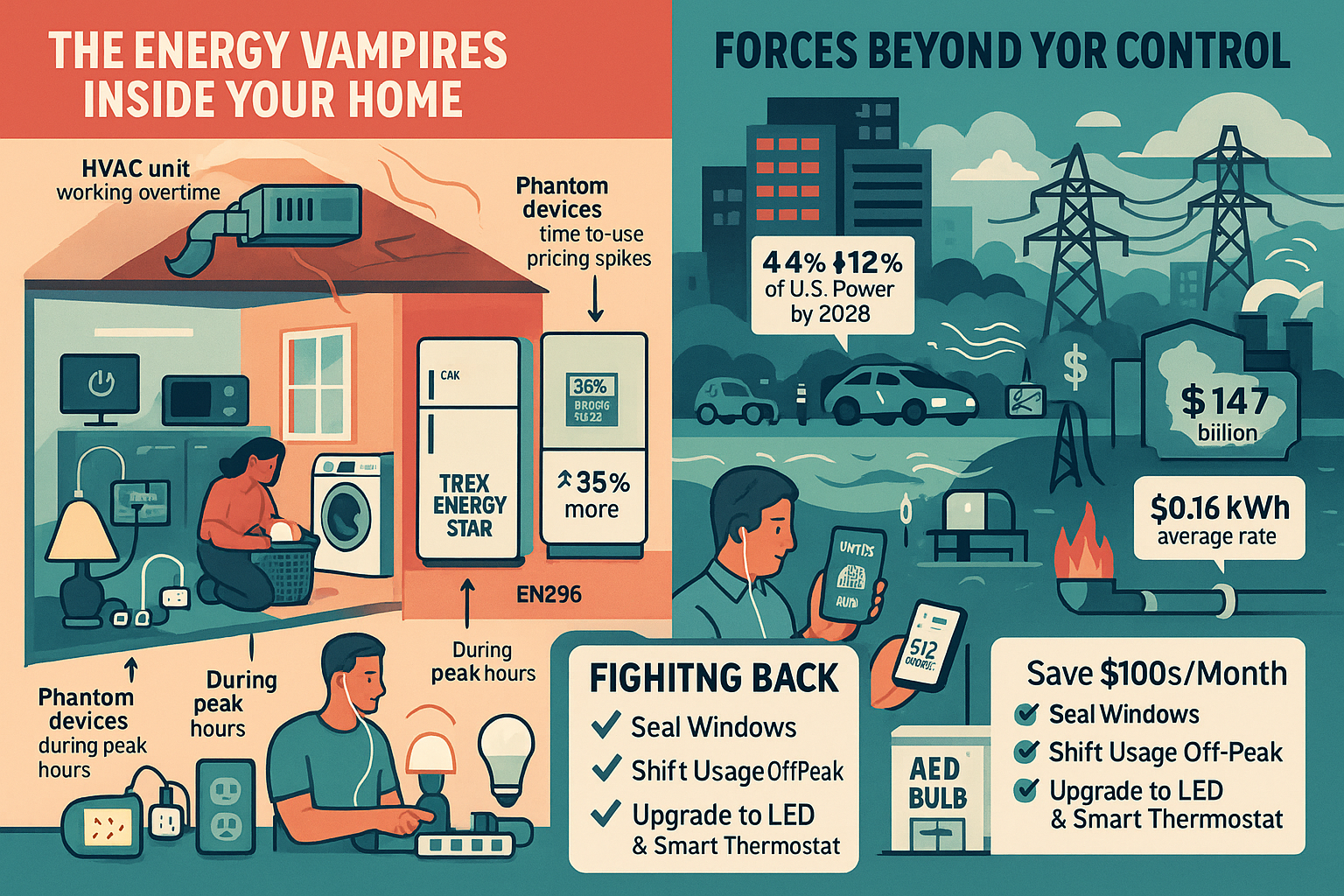
The Silent Energy Vampires in Your Home
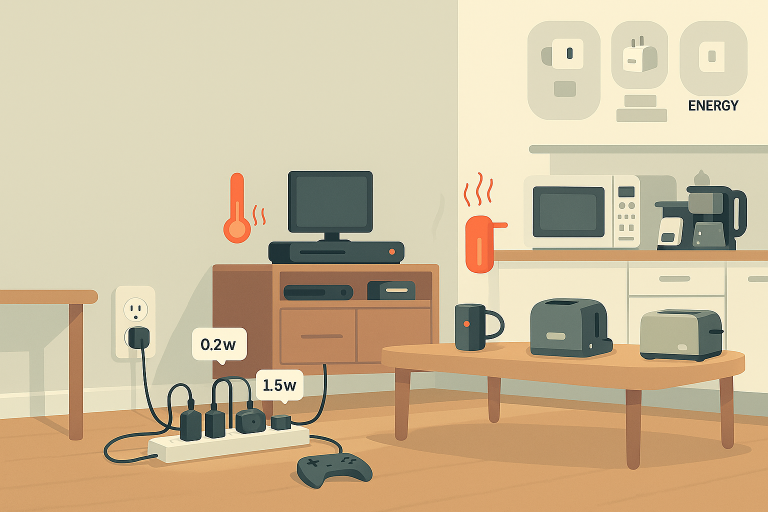
Even if you think you’re being careful with energy, there are sneaky ways power gets used without you realizing it. These are called energy vampires, and they’re quietly driving up your bill.
1. Your HVAC System (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning)
Your heating and cooling system uses about half of your monthly electric bill — that’s the biggest chunk. If your system is old or hasn’t been maintained, it’s working harder than it should, using more electricity.
- A unit older than 10 years may lack modern efficiency features.
- Not changing filters or skipping maintenance can reduce its efficiency by up to 30%.
- Regular check-ups and cleaning can save you money in the long run.
2. Phantom Power Drain (Also Known as “Vampire Devices”)
Those little red lights on your TV, phone chargers left plugged in, or game consoles still draw power even when they’re off. This is called phantom load or vampire energy.
- Studies show these devices can account for 10% of your home’s total electricity use.
- The average home has around 40 devices constantly drawing power.
- That could cost you $100 or more per year, just from devices you’re not even using!
Tip: Use smart power strips or unplug devices when not in use.
3. Poor Insulation and Drafts
If your house isn’t properly sealed, the air you pay to heat or cool can escape through windows, doors, or the attic.
- Bad insulation can raise your heating/cooling costs by 20% or more during extreme weather.
- The attic is often the worst offender — like a giant open window for your expensive air.
Tip: Seal gaps, add insulation, and consider replacing old windows.
4. Peak Hour Pricing
Some utility companies charge more during certain times of the day — usually weekday afternoons and evenings — known as peak hours.
- Running appliances like your dishwasher, dryer, or EV charger during these hours can cost 2–3 times more than off-peak times (like late at night).
Tip: Check with your utility company for off-peak hours and try to shift usage to those times.
5. Old Appliances and Inefficient Lighting
Older appliances, especially refrigerators over 10 years old, use 35% more electricity than newer models.
- Refrigeration alone can take up 10–20% of your total bill.
- Traditional light bulbs waste 90% of their energy as heat. LEDs are much more efficient and can save you over $100 a year.
Tip: Upgrade to ENERGY STAR appliances and LED lighting.
External Factors Causing Higher Bills
Even if you’re doing everything right, there are bigger forces at play that affect your electricity bill:
1. Rising Electricity Rates
Electricity prices are going up fast. In 2023, the national average was 16 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh) — a 24% increase since 2019.
- Utilities are raising rates due to complex pricing models like tiered billing and seasonal charges.
- Experts expect another 13% increase nationwide between 2022 and 2025, adding about $219 to the average annual bill.
2. Aging Power Grid and Infrastructure Costs
The U.S. electrical grid is getting old, and fixing it is expensive.
- Transmission and distribution costs (getting power to your home) are rising twice as fast as inflation.
- Components like transformers have gotten 75% more expensive since 2019.
- Utilities often pass these costs directly to consumers — plus they earn a profit (around 10%) on infrastructure investments.
3. More Demand from Data Centers and Electric Vehicles
As we rely more on digital services and clean energy, demand for electricity is surging.
- Data centers (which power cloud computing and AI) are expected to use up to 12% of all U.S. electricity by 2028 — up from 4.4% today.
- More electric vehicles (EVs) and heat pumps mean more pressure on the grid, especially during peak times.
4. Fossil Fuel Prices and Market Failures
Even though renewable energy is growing, many power plants still rely on fossil fuels like natural gas.
- Global events (like wars or supply chain issues) cause big swings in fuel prices.
- In 2024, a major regional grid operator (PJM) found that 26 gigawatts of fossil fuel capacity was unreliable during extreme weather.
- That caused a $14.7 billion cost passed to customers, leading to at least a 10% bill increase in some areas.
5. Climate Change
A warmer planet means more air conditioning use, longer heat waves, and more strain on the grid.
- During extreme heat, air conditioning alone can cost $150–$200/month.
- Hotter temperatures also make appliances like fridges work harder.
- Climate-related disasters (like wildfires or storms) damage power lines and equipment — and those repairs are paid for by customers.
What You Can Do: Practical Tips to Cut Your Bill
Even with all these challenges, there are steps you can take to lower your electricity bill and regain control.
1. Eliminate Phantom Loads and Optimize Usage
- Use smart power strips to cut power to devices when not in use.
- Unplug chargers and small electronics when not needed.
- Switch to LED bulbs — they last longer and use way less energy.
- Run large appliances (dishwasher, washing machine, etc.) during off-peak hours.
- Only run full loads to avoid wasting water and energy.
2. Improve Your Home’s Efficiency
- Seal leaks around windows, doors, and outlets using caulk or weatherstripping.
- Add attic insulation — this is one of the most cost-effective upgrades.
- Consider replacing old windows with energy-efficient ones.
- Get a professional energy audit (often subsidized by government programs) to find hidden problems.
3. Maintain and Upgrade Your HVAC System
- Replace air filters every 1–3 months.
- Schedule annual maintenance to keep your system running efficiently.
- Install a smart thermostat to automatically adjust temperatures when you’re away or asleep. This can save 10% or more on heating and cooling.
- Consider upgrading to an ENERGY STAR model if your system is over 10 years old.
- Replace old electric heaters with heat pumps, which are much more efficient and can save $1,000+ annually.
4. Explore Alternative Energy Options
- Solar panels can provide long-term savings and protect you from future rate hikes. Take advantage of the 30% Federal Tax Credit.
- If rooftop solar isn’t possible, look into community solar programs, which offer discounts on your regular bill.
- In deregulated markets, switch to a fixed-rate plan to lock in a stable price.
- Compare energy providers to see if you can get a better deal.
5. Advocate for Larger Changes
While individual actions help, real change needs to come from policy and regulation.
- Support efforts to modernize the power grid and expand renewable energy sources.
- Push for reforms that ensure utility investments improve reliability and affordability — not just profits.
- Help promote energy assistance programs for low-income families who are hit hardest by rising bills.
Regional Electricity Cost Differences
Electricity prices vary widely depending on where you live. Here’s a breakdown for March 2025:
| Region | Avg. Cost per kWh | Projected Increase (2022–2025) | Key Reasons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific | ~21¢ or more | 26% | Wildfire mitigation, regulations |
| New England | ~20¢ or more | ~10%+ | Heavy reliance on natural gas |
| Middle Atlantic | ~18¢ or more | >13% | PJM costs, dense population |
| West North Central | ~11¢ | 8% | More coal, less population density |
| Hawaii | 41¢ | N/A | Remote location, imported fuel |
Knowledge = Power (and Savings!)
Your rising electricity bill isn’t just about how much power you use — it’s also about outdated systems, volatile markets, climate change, and surging demand from new technologies.
But now that you understand the causes, you can start fighting back.
- Start with small changes at home: eliminate phantom loads, shift appliance use, seal drafts, and maintain your HVAC.
- Look into solar options or fixed-rate plans for long-term stability.
- And don’t forget — advocating for smarter policies and cleaner energy can help everyone save in the future.
The next shocking bill might just be the push you need to take control of your energy future.